Treatment GuideJust DiagnosedSex & DatingAfrican AmericanStigmaAsk the HIV DocPrEP En EspañolNewsVoicesPrint IssueVideoOut 100
CONTACTCAREER OPPORTUNITIESADVERTISE WITH USPRIVACY POLICYPRIVACY PREFERENCESTERMS OF USELEGAL NOTICE
© 2025 Pride Publishing Inc.
All Rights reserved
All Rights reserved
By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
HIVers in France who do not have a permanent job or a steady relationship have a higher risk of being hospitalized during early HIV disease than their coupled or steadily employed peers, researchers reported in the October 1 edition of the Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. A study of 319 HIV patients between 1996 and 2002 showed that 84 were hospitalized and three died. Study subjects with temporary employment, who were unpartnered, or both were significantly more likely to have been hospitalized during the first few months of HIV infection. Having a mental disorder or depression or a history of injection-drug use also was linked with a greater chance of being hospitalized. The researchers theorize that poor social or economic conditions could lead to stress, which in turn can weaken the body's immune system defenses or increase such unhealthy practices as tobacco, alcohol, and drug use.
From our Sponsors
Most Popular
BREAKING: Supreme Court rules to save free access to preventive care, including PrEP
June 27 2025 10:32 AM
Thanks to U=U, HIV-positive people can live long, happy, healthy lives
July 25 2025 2:37 PM
Plus: Featured Video
Latest Stories
Amazing People of 2025: Javier Muñoz
October 17 2025 7:35 PM
It’s National PrEP Day! Learn the latest about HIV prevention
October 10 2025 9:00 AM
“I am the steward of my ship”: John Gibson rewrites his HIV narrative
September 16 2025 2:56 PM
“So much life to live”: Eric Nieves on thriving with HIV
September 03 2025 11:37 AM
The Talk: Owning your voice
August 25 2025 8:16 PM
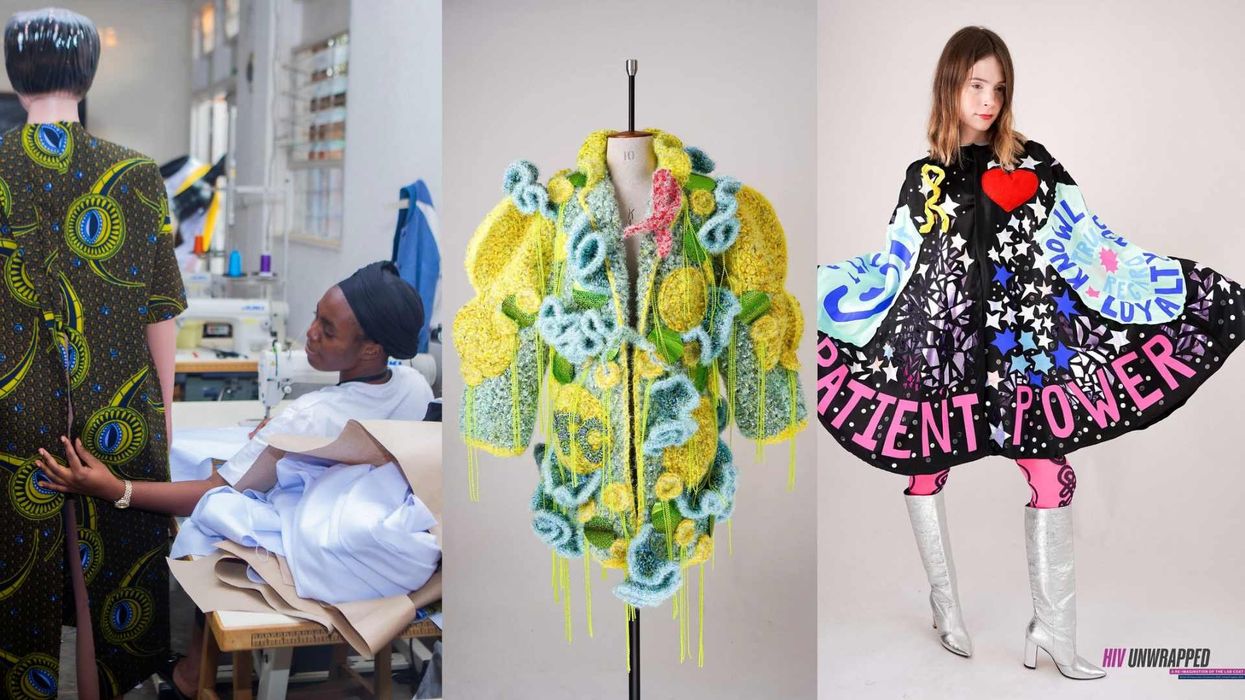
The lab coat just got queer
August 21 2025 10:00 AM
Messenger RNA could be the key to an HIV vaccine — but government cuts pose a threat
August 20 2025 8:02 AM
The Talk: Beyond the exam room
August 13 2025 3:15 PM
The Talk: Navigating your treatment
August 01 2025 6:02 PM
The Talk: Starting the conversation
July 25 2025 4:47 PM
How the Black AIDS Institute continues to fill in the gaps
July 25 2025 1:06 PM
“I felt like a butterfly”: Niko Flowers on reclaiming life with HIV
July 23 2025 12:22 PM
Dancer. Healer. Survivor. DéShaun Armbrister is all of the above
July 02 2025 8:23 PM
1985: the year the AIDS crisis finally broke through the silence
June 26 2025 11:24 AM
VIDEO: A man living with HIV discusses his journey to fatherhood
June 10 2025 4:58 PM
Trump admin guts $258 million in funding for HIV vaccine research
June 03 2025 3:47 PM
Grindr is reminding us why jockstraps are so sexy and iconic
May 02 2025 5:36 PM
HRC holds 'die-in' to protest Trump health care cuts
April 28 2025 2:11 PM
Trending stories
Recommended Stories for You