March 08 2010 12:00 AM EST
Treatment GuideJust DiagnosedSex & DatingAfrican AmericanStigmaAsk the HIV DocPrEP En EspañolNewsVoicesPrint IssueVideoOut 100
CONTACTCAREER OPPORTUNITIESADVERTISE WITH USPRIVACY POLICYPRIVACY PREFERENCESTERMS OF USELEGAL NOTICE
© 2025 Pride Publishing Inc.
All Rights reserved
All Rights reserved
By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
University of Michigan scientists have identified a new reservoir for hidden HIV-infected cells that can serve as a factory for new infections. The findings, which appear online March 7 in Nature Medicine, indicate a new target for curing the disease so those infected with the virus may someday no longer rely on AIDS drugs for a lifetime.
"Antiviral drugs have been effective at keeping the virus at bay. However once the drug therapy is stopped, the virus comes back," says senior author of the study Kathleen L. Collins, MD, Ph.D., associate professor of both internal medicine and microbiology and immunology at the U-M Medical School.
In people infected with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus), the virus that causes AIDS, there's an unsolved problem with current antiviral drugs. Though lifesaving, they cannot root the virus out of the body. Infected cells are able to live on, undetected by the immune system, and provide the machinery for the virus to reproduce and spread.
Important new research by U-M has discovered that bone marrow, previously thought to be resistant to the virus, can contain latent forms of the infection.
"This finding is important because it helps explain why it's hard to cure the disease," Collins says. "Ultimately to cure this disease, we're going to have to develop specific strategies aimed at targeting these latently infected cells."
"Currently people have to take antiviral drugs for their entire life to control the infection," she says. "It would be easier to treat this disease in countries that don't have the same resources as we do with a course of therapy for a few months, or even years. But based on what we know now people have to stay on drugs for their entire life."
Using tissue samples, U-M researchers detected HIV genomes in bone marrow isolated from people effectively treated with antiviral drugs for more than six months.
While further studies are needed to demonstrate that stem cells can harbor the HIV virus, the study results confirm that HIV targets some long-lived progenitor cells, young cells that have not fully developed but mature into cells with special immune functions. When active infection occurs the toxic effects of the virus kill the cell even as the newly made viral particles spread the infection to new target cells.
"Our finding that HIV infects these cells has clear ramifications for HIV disease because some of these cells may be long-lived and could carry latent HIV for extended periods of time," she says. "These HIV cell reservoirs can be induced to generate new infections."
The new research gives a broader view of how HIV overwhelms the body's immune system and devastates its ability to regenerate itself.
Globally more than 30 million people are infected with HIV, including millions of children. Improvements have been made since the 1990s in the way the disease is treated that has led to an 85 percent to 90 percent reduction in mortality.
"Drugs now available are effective at treating the virus, making HIV more of a chronic disease than a death sentence," Collins says. "This has made a huge impact in quality of life, however only 40 percent of people worldwide are receiving anti-viral drugs and unfortunately that means that not everybody is benefiting."
From our Sponsors
Most Popular
“So much life to live”: Eric Nieves on thriving with HIV
September 03 2025 11:37 AM
Thanks to U=U, HIV-positive people can live long, happy, healthy lives
July 25 2025 2:37 PM
The Talk: Beyond the exam room
August 13 2025 3:15 PM
BREAKING: Supreme Court rules to save free access to preventive care, including PrEP
June 27 2025 10:32 AM
Messenger RNA could be the key to an HIV vaccine — but government cuts pose a threat
August 20 2025 8:02 AM
“I felt like a butterfly”: Niko Flowers on reclaiming life with HIV
July 23 2025 12:22 PM
Dancer. Healer. Survivor. DéShaun Armbrister is all of the above
July 02 2025 8:23 PM
The Talk: Starting the conversation
July 25 2025 4:47 PM
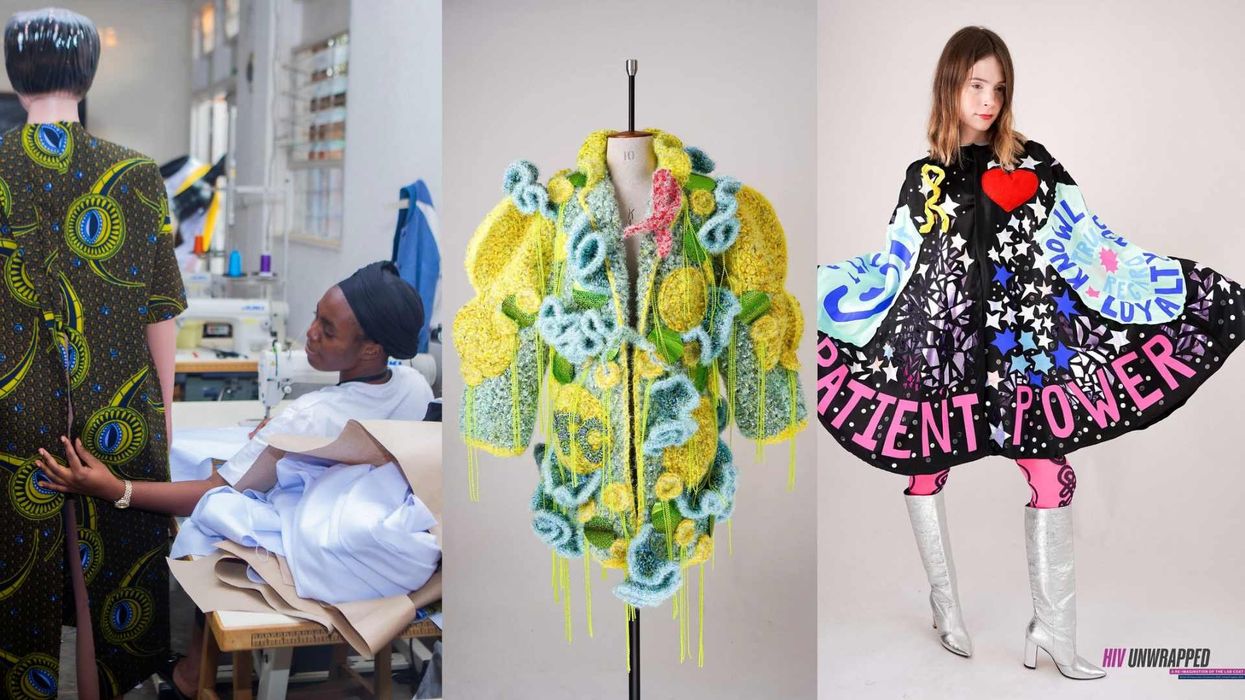
The lab coat just got queer
August 21 2025 10:00 AM
Plus: Featured Video
Latest Stories
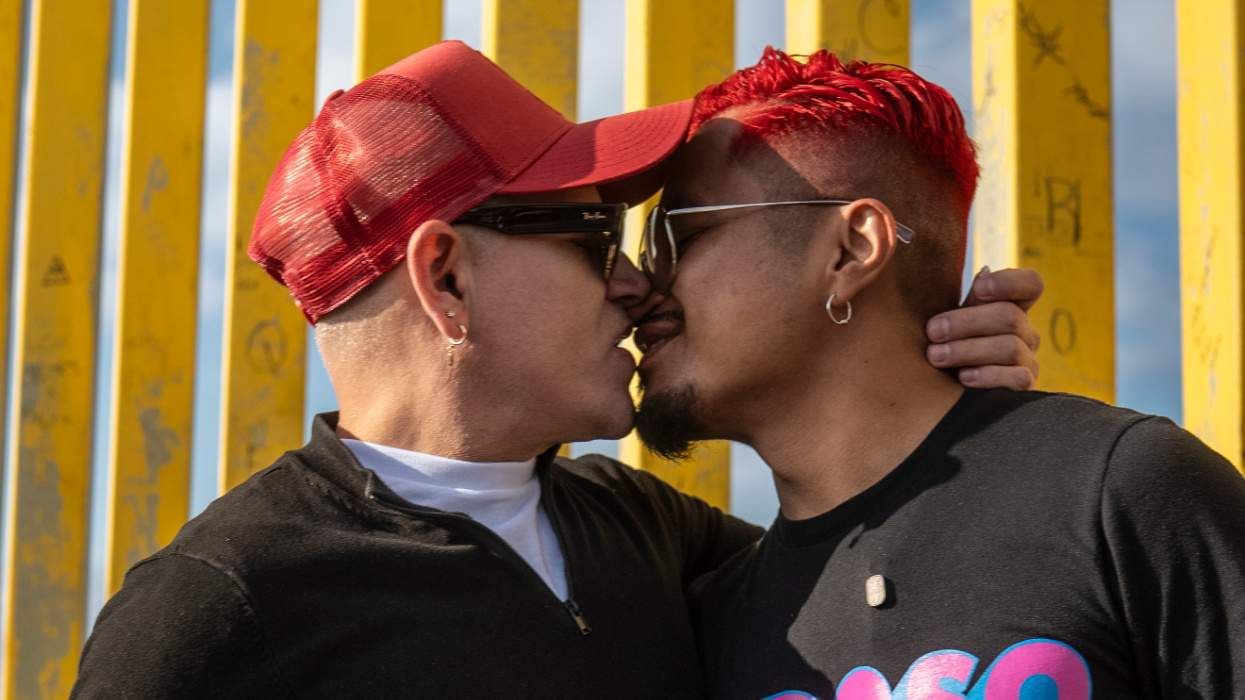
HIV-positive men stage 'Kiss-In' protest at U.S.-Mexico border
December 01 2025 12:56 PM
What the AIDS crisis stole from Black gay men
December 01 2025 6:00 AM
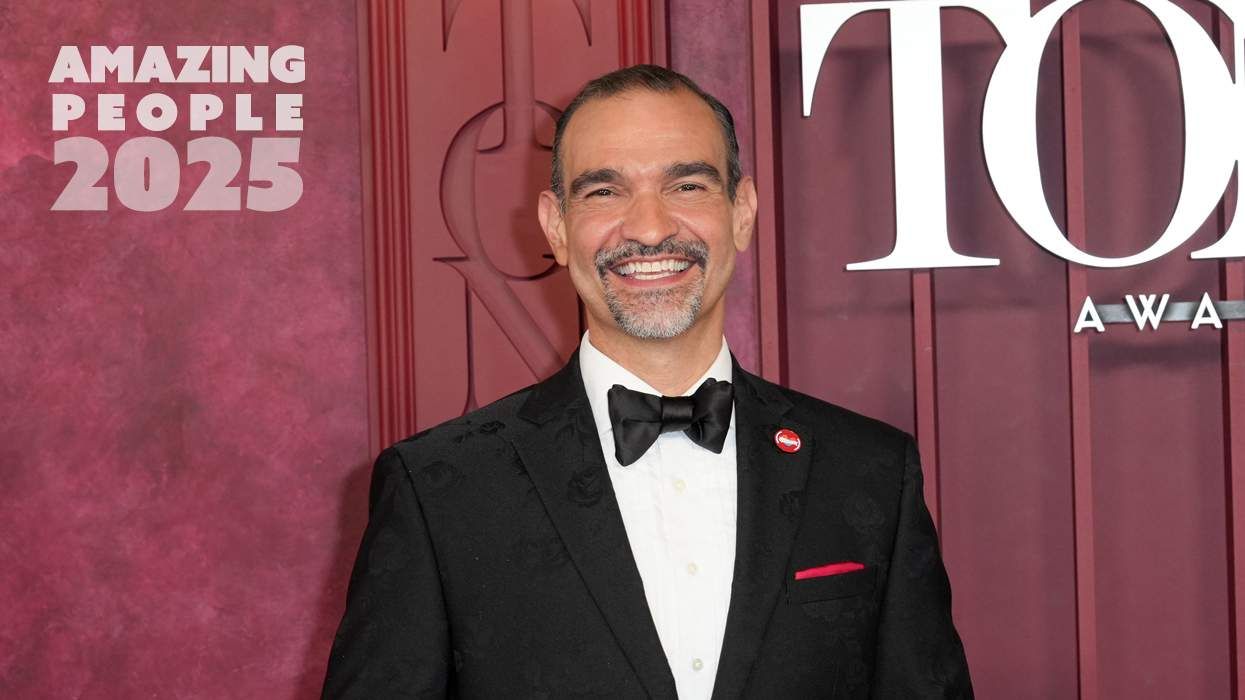
Amazing People of 2025: Javier Muñoz
October 17 2025 7:35 PM
It’s National PrEP Day! Learn the latest about HIV prevention
October 10 2025 9:00 AM
“I am the steward of my ship”: John Gibson rewrites his HIV narrative
September 16 2025 2:56 PM
The Talk: Owning your voice
August 25 2025 8:16 PM
The Talk: Navigating your treatment
August 01 2025 6:02 PM
How the Black AIDS Institute continues to fill in the gaps
July 25 2025 1:06 PM
1985: the year the AIDS crisis finally broke through the silence
June 26 2025 11:24 AM
VIDEO: A man living with HIV discusses his journey to fatherhood
June 10 2025 4:58 PM
Trump admin guts $258 million in funding for HIV vaccine research
June 03 2025 3:47 PM
Grindr is reminding us why jockstraps are so sexy and iconic
May 02 2025 5:36 PM
HRC holds 'die-in' to protest Trump health care cuts
April 28 2025 2:11 PM
Two right-wing Supreme Court justices signal they may uphold access to PrEP and more
April 21 2025 4:10 PM
500,000 Children at Risk: PEPFAR Funding Crisis
April 08 2025 3:51 PM
Broadway's best raise over $1 million for LGBTQ+ and HIV causes
April 03 2025 7:15 PM
The Talk Season 5 premieres this spring with HIV guidance for the newly diagnosed
March 26 2025 1:00 PM