September 17 2010 6:50 PM EST
Treatment GuideJust DiagnosedSex & DatingAfrican AmericanStigmaAsk the HIV DocPrEP En EspañolNewsVoicesPrint IssueVideoOut 100
CONTACTCAREER OPPORTUNITIESADVERTISE WITH USPRIVACY POLICYPRIVACY PREFERENCESTERMS OF USELEGAL NOTICE
© 2026 Pride Publishing Inc.
All Rights reserved
All Rights reserved
By continuing to use our site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use.
Your friends are probably more popular than you are. And this "friendship paradox" may help predict the spread of infectious disease, according to a study published in the journal PLoS One.
Nicholas Christakis, professor of medicine, medical sociology, and sociology at Harvard University, and James Fowler, professor of medical genetics and political science at the University of California, San Diego, used the paradox to study the 2009 flu epidemic among 744 students. The findings, the researchers say, point to a novel method for early detection of contagious outbreaks.
Analyzing a social network and monitoring the health of its central members is an ideal way to predict an outbreak. But such detailed information simply doesn't exist for most social groups, and producing it is time-consuming and expensive.
The "friendship paradox," first described in 1991, potentially offers an easy way around this. Simply put, the paradox states that, statistically, the friends of any given individual are likely more popular than the individual herself. Take a random group of people, ask each of them to name one friend, and on average the named friends will rank higher in the social web than the ones who named them.
If this is hard to fathom, imagine a large cocktail party with a host holding court in the center while, at the fringes, a few loners lean against the walls staring at their drinks. Randomly ask the partygoers to each name a friend, and the results will undoubtedly weigh heavily in the direction of the well-connected host. Few people will name a recluse.
And just as they come across gossip, trends and good ideas sooner, the people at the center of a social network are exposed to diseases earlier than those at the margins.
As the 2009 influenza season approached, Christakis and Fowler decided to put these basic features of a social network to work, contacting 319 Harvard undergraduates who in turn named a total of 425 friends. Monitoring the two groups both through self-reporting and data from Harvard University Health Services, the researchers found that, on average, the friends group manifested the flu roughly two weeks prior to the random group using one method of detection, and a full 46 days prior to the epidemic peak using another method.
"We think this may have significant implications for public health," Christakis says. "Public health officials often track epidemics by following random samples of people or monitoring people after they get sick. But that approach only provides a snapshot of what's currently happening. By simply asking members of the random group to name friends, and then tracking and comparing both groups, we can predict epidemics before they strike the population at large. This would allow an earlier, more vigorous, and more effective response."
"If you want a crystal ball for finding out which parts of the country are going to get the flu first, then this may be the most effective method we have now," Fowler says. "Currently used methods are based on statistics that lag the real world or, at best, are contemporaneous with it. We show a way you can get ahead of an epidemic of flu, or potentially anything else that spreads in networks."
Indeed, the authors note that the same method could be used very widely to anticipate epidemics of behaviors like drug use or even the diffusion of ideas or fashions.
John Glasser, a mathematical epidemiologist at the Centers for Disease Control in Atlanta (who was not involved in this research), says, "Christakis's and Fowler's provocative study should cause infectious disease epidemiologists and public health practitioners alike to consider the social contexts within which pathogens are transmitted. This study may be unique in demonstrating that social position affects one's risk of acquiring disease. Consequently, epidemiologists and social scientists are modeling networks to evaluate novel disease surveillance and infection control strategies."
From our Sponsors
Most Popular
“So much life to live”: Eric Nieves on thriving with HIV
September 03 2025 11:37 AM
The Talk: Beyond the exam room
August 13 2025 3:15 PM
Messenger RNA could be the key to an HIV vaccine — but government cuts pose a threat
August 20 2025 8:02 AM
It’s National PrEP Day! Learn the latest about HIV prevention
October 10 2025 9:00 AM
Amazing People of 2025: Javier Muñoz
October 17 2025 7:35 PM
The lab coat just got queer
August 21 2025 10:00 AM
The Talk: Owning your voice
August 25 2025 8:16 PM
“I am the steward of my ship”: John Gibson rewrites his HIV narrative
September 16 2025 2:56 PM
Plus: Featured Video
Latest Stories
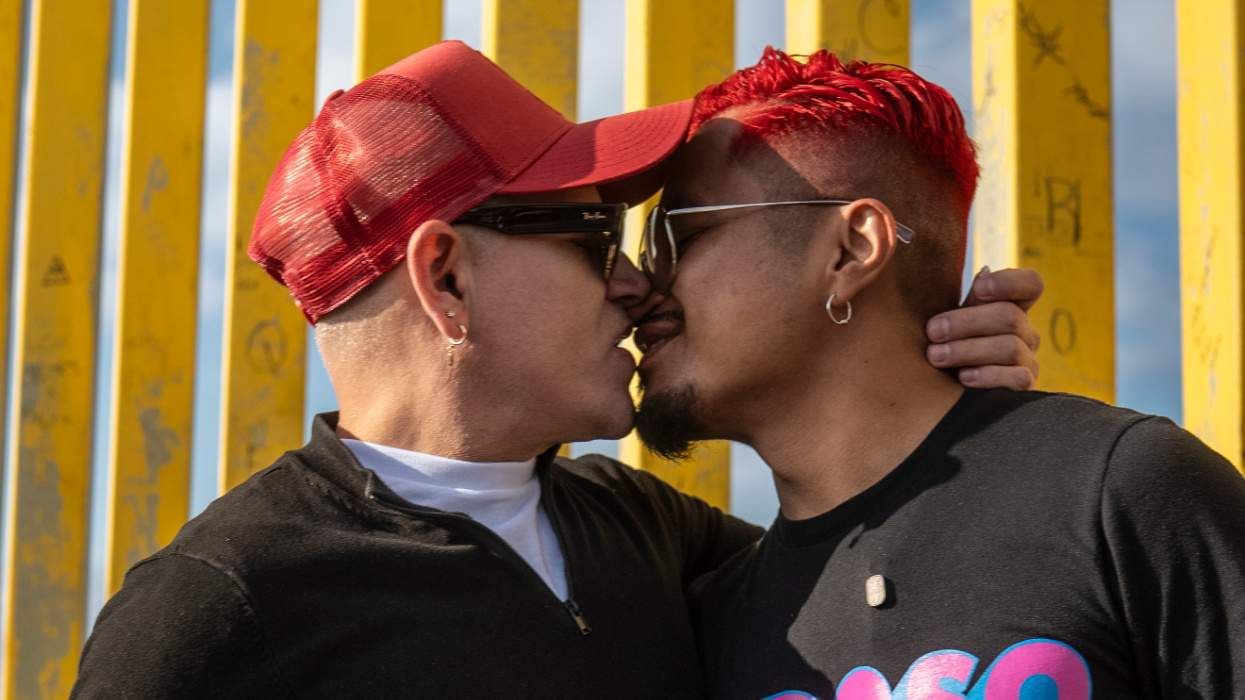
HIV-positive men stage 'Kiss-In' protest at U.S.-Mexico border
December 01 2025 12:56 PM
What the AIDS crisis stole from Black gay men
December 01 2025 6:00 AM
The Talk: Navigating your treatment
August 01 2025 6:02 PM
The Talk: Starting the conversation
July 25 2025 4:47 PM
Thanks to U=U, HIV-positive people can live long, happy, healthy lives
July 25 2025 2:37 PM
How the Black AIDS Institute continues to fill in the gaps
July 25 2025 1:06 PM
“I felt like a butterfly”: Niko Flowers on reclaiming life with HIV
July 23 2025 12:22 PM
Dancer. Healer. Survivor. DéShaun Armbrister is all of the above
July 02 2025 8:23 PM
BREAKING: Supreme Court rules to save free access to preventive care, including PrEP
June 27 2025 10:32 AM
1985: the year the AIDS crisis finally broke through the silence
June 26 2025 11:24 AM
VIDEO: A man living with HIV discusses his journey to fatherhood
June 10 2025 4:58 PM
Trump admin guts $258 million in funding for HIV vaccine research
June 03 2025 3:47 PM
Grindr is reminding us why jockstraps are so sexy and iconic
May 02 2025 5:36 PM
HRC holds 'die-in' to protest Trump health care cuts
April 28 2025 2:11 PM
Two right-wing Supreme Court justices signal they may uphold access to PrEP and more
April 21 2025 4:10 PM
500,000 Children at Risk: PEPFAR Funding Crisis
April 08 2025 3:51 PM